Kalahi-CIDSS
by Jesseshan Marbella | March 7, 2013 11:17 am
Kalahi-CIDSS is implemented by DSWD in partnership with local government units (LGUs). It is designed to empower citizens by honing their capacities to analyze their local situation, identify community needs, and implement small scale community projects in partnership with their LGUs. The success of the community-driven development (CDD) approach is providing an impetus to scale it up into a national program in order to combat poverty in other poor municipalities not previously covered by Kalahi-CIDSS.
Kalahi-CIDSS which stands for Kapit-Bisig Laban sa Kahirapan–Comprehensive and Integrated Delivery of Social Services is the flagship poverty reduction project of the Philippine government which adopts CDD or the Community-Driven Development (people centred approach) as the overall strategy of the project.
Through CDD:
The people themselves decide on the priority needs and the responses to address those needs.
The people design and implement the project themselves.
The people manage the resources to be used in implementing the community projects.
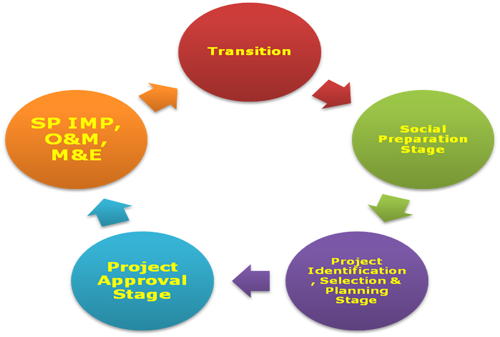
CDD is operationalized through the five-stage, three-cycle community mobilization process called the Community Empowerment Activity Cycle or CEAC. The three cycles are progressive; that each cycle builds on the results and outputs of the previous cycle, towards sustained development. Kalahi-CIDSS is a poverty-reduction project that different agencies and stakeholders at different levels which has been proven to be successful in helping reduce poverty and empowering communities through the employment of participatory method, in many poor areas in the poorest provinces nationwide.
Development Objectives
Reduce Poverty
Community Empowerment
Improve Local Governance
Project Principles
Participation
Transparency
Accountability
CEAC Cycle
 [1]
[1]
The Barangay Assembly The barangay assembly is a gathering of all barangay residents who are at least 15 years old and above, Filipino and listed in the records as members of the barangay assembly (as defined in the Local Government Code, R.A. 7160). It serves as the primary mechanism for the exercise of popular citizenship. It is the foundation where the people can make claims from government over the delivery of basic services and facilities, demand transparency, and even exercise their supreme right to govern.
 [2]
[2]
The Barangay Structure
Among the groups formed during the course of KC implementation include the following:
Participatory Situation Analysis (PSA) Volunteer Teams PSA Volunteer Team is a group composed of at least 2 community residents per purok. Potential PSA volunteers can be nominated during the first barangay assembly, where they shall be formally selected. PSA volunteers share information about local conditions through the use of visual tools.
Barangay Representation Teams (BRT) Elected by the BA during the meeting to validate the results of the PSA (Step 4) this three-member team is the official delegation of the barangay to the Municipal Inter-Barangay Forum (MIBF). The BRT is vested with authority to vote (for and in behalf of the barangay) on all matters brought before the attention of the MIBF, especially those concerning the prioritization of projects to be funded. The team is also the official barangay representative to the workshop for the setting of criteria to be used in the prioritization/ranking of proposed sub-projects.
Project Preparation Teams (PPT) The team shall develop the sub-project concept paper based on the ideas generated by the Barangay Assembly (BA). Once the sub-project concept is considered by the MIBF for funding, the team shall proceed with the preparation of the detailed sub-project proposal with assistance from the Municipal Inter Agency Committee (MIAC) or from persons with technical skills required by the sub-project. The three members of the team will be elected by the BA during the meeting to validate the results of the PSA
Community-Based Monitoring Team (CBMT) The team shall monitor the progress of sub-project implementation. It shall validate the physical accomplishments based on reports prepared by the Implementation Team and the approved detailed work and financial plan. The team shall also ensure that deliveries of items or goods purchased are properly stored. Like the other teams, the three members of the MIT are elected by the BA (in the step 10 of the sub-project cycle).
Barangay Sub-Project Management Committees (BSPMCs) The committee shall take care of the overall management of the sub-project. Under the guidance of the Barangay Development Council (BDC), it shall also formulate policies and make decisions for the project. It shall oversee sub-project implementation, monitoring, maintenance and sustainability after project completion. The Chairman of the BSPMC shall be elected by the Barangay Assembly (BA) during the feedback meeting on the results of the Municipal Inter-Barangay Forum (MIBF) ranking of sub-projects concepts. The secretary, bookkeeper, members of the Audit and Inventory Team (AIT), Project Implementation Team (PIT), Monitoring and Inspection Team (MIT) and the Procurement Team (PT) shall likewise be elected by the BA during the said meeting. However, the Treasurer of the barangay council automatically becomes the treasurer of the BSPMC. The heads of the committees, team and staff of the Sub Project Organization shall constitute the Executive Committee of the BSPMC.
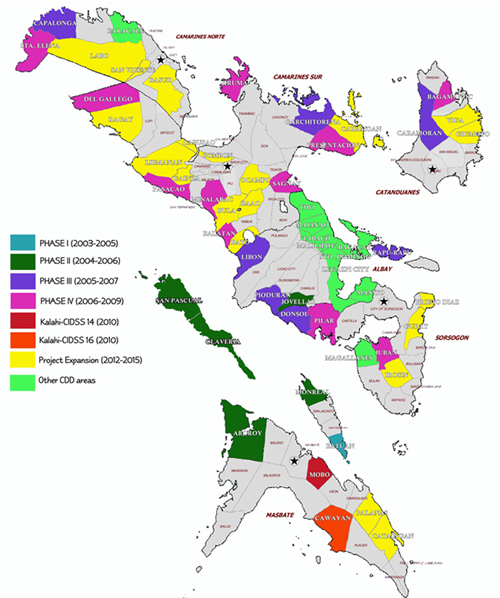
Project Areas
 [3]
[3]
- [Image]: https://fo5.dswd.gov.ph/wp-content/uploads/2013/03/CEAC-CYCLE-.png
- [Image]: https://fo5.dswd.gov.ph/wp-content/uploads/2013/03/Untitled-1.jpg
- [Image]: https://fo5.dswd.gov.ph/wp-content/uploads/2013/03/Kalahi-CIDSS-Areas-2003-2012.jpg
Source URL: https://fo5.dswd.gov.ph/programs-services/core-programs/community-driven-development-program-kalahi-cidss/